The term “profile” has several different meanings in the English language. It can refer to the side view of a shape, a characteristic appearance, or the data of a user in a computer application. In a technical context, it describes the longitudinal section, cross section or contour, as well as the structure of a running surface.
Profiles in various designs can be found in every household, for example in window frames, door seals, picture frames, in bathroom or kitchen areas, on floors and ceilings. In industrial applications, a profile is an object made of metal, wood or plastic in the form of a bar that has the same cross section along its entire length. The different profile types are named according to their cross section, their function or their application.
Designation by Cross Section
Profiles can be classified according to their cross section. Depending on the cross-sectional shape, there are flat profiles, edge profiles, round profiles, mixed profiles, half-round profiles and flag profiles.
In addition to the cross-sectional geometry, a distinction is made between solid and hollow profiles, the latter also known as hollow chamber profiles. Hollow profiles are hollow inside or not completely closed. Solid profiles are massive and have no cavity.
Accordingly, technical profiles with a rectangular or square cross section are referred to as rectangular profiles, those with a triangular cross section as triangular profiles, and hexagonal ones as hexagonal profiles. Rectangular profiles are also referred to as rectangular tubes or square tubes if the cross section is square. Angular edge profiles include angle profiles such as L profiles, T profiles, U profiles and H profiles.


Flag profiles, also known as keder profiles, have a round or angular cross section with a flat profile on one side. The round or angular part can be solid or hollow. Mixed profiles, as used for example in window construction, can have very different and complex cross sections.
Manufacturing of Profiles
The production of metal profiles and plastic profiles is carried out using forming processes. In the case of metal profiles, the process is called extrusion (German: Strangpressen), while for plastic profiles the term extrusion is also used. Both processes are based on the same principle.
The geometry of the die determines the cross section of the extruded strand. For the production of hollow profiles, dies with differently shaped mandrels are used. After extrusion, a cooling process is often required so that the still-hot extruded bar retains its shape and does not collapse or bend. Typical extrusion speeds for aluminum profiles are in the range of 5 to 50 meters per minute[1].
Materials and Fields of Application
The properties of the materials from which the various profile types are made determine their areas of application.
Wood Profiles
Wood profiles are mainly used in interior construction and are usually referred to as moldings rather than profiles. They serve as baseboards, decorative moldings, corner moldings, ceiling moldings, edge protection strips, stair edge moldings, finishing strips and handrails.
Metal Profiles
Metal profiles are predominantly made of aluminum, stainless steel and steel. They are mainly used in the construction industry as well as for railings, ladders and other bracing elements.
Stainless steel profiles are available in most common profile types. As round tubes, they are used in structural engineering. Bracing elements, railings and handrails as well as flagpoles are manufactured from them. Square tubes or U profiles are used for signs, frame structures or clothes rails. Angle profiles are often used as finishing strips.

Aluminum profiles, like their stainless steel counterparts, are available in many different types. However, aluminum is significantly more cost-effective, lighter and easier to process than stainless steel and therefore has a wider range of applications. In private settings, aluminum profiles are found in windows and doors, in substructures for roof and terrace construction, for framing photovoltaic systems, in drywall construction and interior finishing. Floor moldings, ceiling moldings, wall moldings, curtain rails and other fastening elements are manufactured from this material. In industrial applications, aluminum profiles are used in mechanical engineering, structural engineering, façade construction and automotive engineering.
Plastic Profiles
Plastic profiles are made from thermoplastics, elastomers and thermoplastic elastomers, as well as glass fiber reinforced plastics (GFRP). The profile type and its application depend on the typical properties of the plastics.
Thermoplastic Profile Types
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polycarbonate (PC), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyamide (PA) are among the thermoplastics.
Flat profiles, round profiles, edge profiles and angle profiles are manufactured from these polymers.
PMMA and PC are also scratch-resistant and transparent. Products made from these plastics are used in the lighting, advertising, display and automotive industries. Polycarbonate, which is stable in a temperature range from -100 °C to +110 °C and has a high surface gloss, is also used for roof constructions, aircraft construction and façade construction.

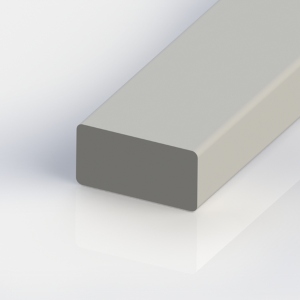
Rigid PVC (PVC-U) has high impact strength and scratch resistance, is weather-resistant and flame-retardant. PVC profiles are cost-effective and ideally suited for use in the construction industry. They are found in window constructions, greenhouses and furniture, and are also used in the construction of ventilation systems and cable ducts.
The polyolefins polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) have good chemical resistance, high impact strength and good hardness. Their density is comparatively low and they are halogen-free. The fields of application are diverse: PP and PE profiles are used in container construction for the food industry, in medical technology and in the construction industry for window, door and roof structures.
Profiles Made of Elastomers
Elastomers are rubber-elastic, non-melting and do not have thermoplastic properties. Examples include natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), nitrile rubber (NBR), chloroprene rubber (CR), fluoro rubber (FKM), butadiene rubber (BR), ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) and silicone rubber. In contrast to other profile types, rubber profiles yield an intermediate product after extrusion, which is then brought into its final form through subsequent vulcanization.
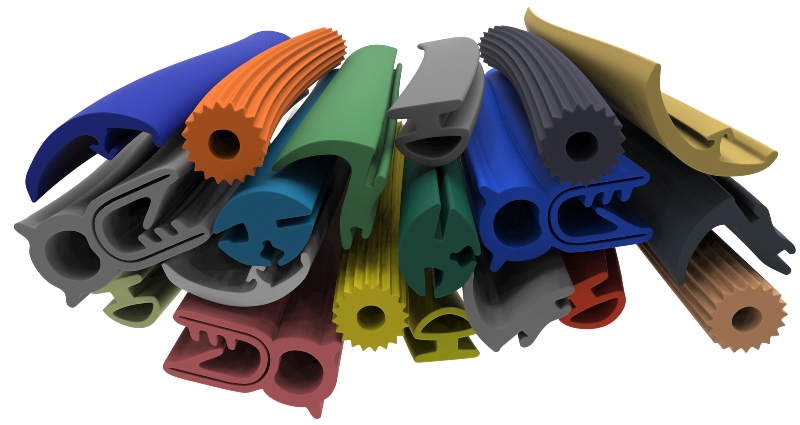

Depending on resistance to heat, cold, weathering and contact media, as well as fire protection requirements and approvals for the food and medical sectors, a suitable elastomer material can be selected. Installation parameters such as installation method and pressure determine the profile cross section, which can be very complex.
They are mainly used as seals in façade, door, window and residential construction, as well as in ventilation and air conditioning technology, the food industry, process engineering and the automotive industry.
Silicone rubber is stable over a wide temperature range from -60 °C to 250 °C. For this reason, silicone profiles are suitable for use in ovens, steam cookers and freezers.
Foam rubber and cellular rubber profiles, made from various polymers and also known as porous rubber, are produced by adding blowing agents to natural or synthetic rubber. Foam rubber has open cells and a dense outer skin, while cellular rubber has no outer skin but closed cells. For this reason, cellular rubber is water- and airtight. Both materials are used to manufacture round cords, edge profiles, angle profiles, keder profiles and special profiles. These products are used for sealing, insulating and damping in window and door construction, ventilation technology and sound systems.
Elastoplastic Profile Types
Thermoplastic elastomers are soft to hard plastics that are elastic at room temperature and can be deformed when heat is applied. They are fusible and therefore formable and can be welded. They are also referred to as elastoplastics, abbreviated as TPE or TPR, derived from the English term “thermoplastic rubber”.
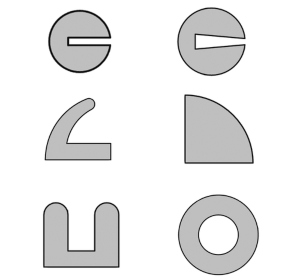
Many thermoplastic elastomers are UV- and weather-resistant, electrically insulating, FDA compliant, antimicrobial, self-extinguishing, halogen- and silicone-free, as well as recyclable. In addition, as rubber-like materials they have a high elastic recovery. All common profile types can be manufactured from TPE. TPE profiles are used as seals and edge protection in plastic housings, in the automotive industry, electrical engineering, the food industry and the pharmaceutical industry.
The wide variety of profile types and the large selection of materials make it possible to find a suitable profile for virtually any requirement.
Source: 1) https://www.techpilot.de/lexikon/strangpressen/
Image sources: Cover image | © DmyTo – stock.adobe.com Aluminum profiles in window construction | © S.J.Takemoto - CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=19810881 Extruded elastomer profiles | © frog – stock.adobe.com
 Reichelt Chemietechnik Magazine
Reichelt Chemietechnik Magazine
